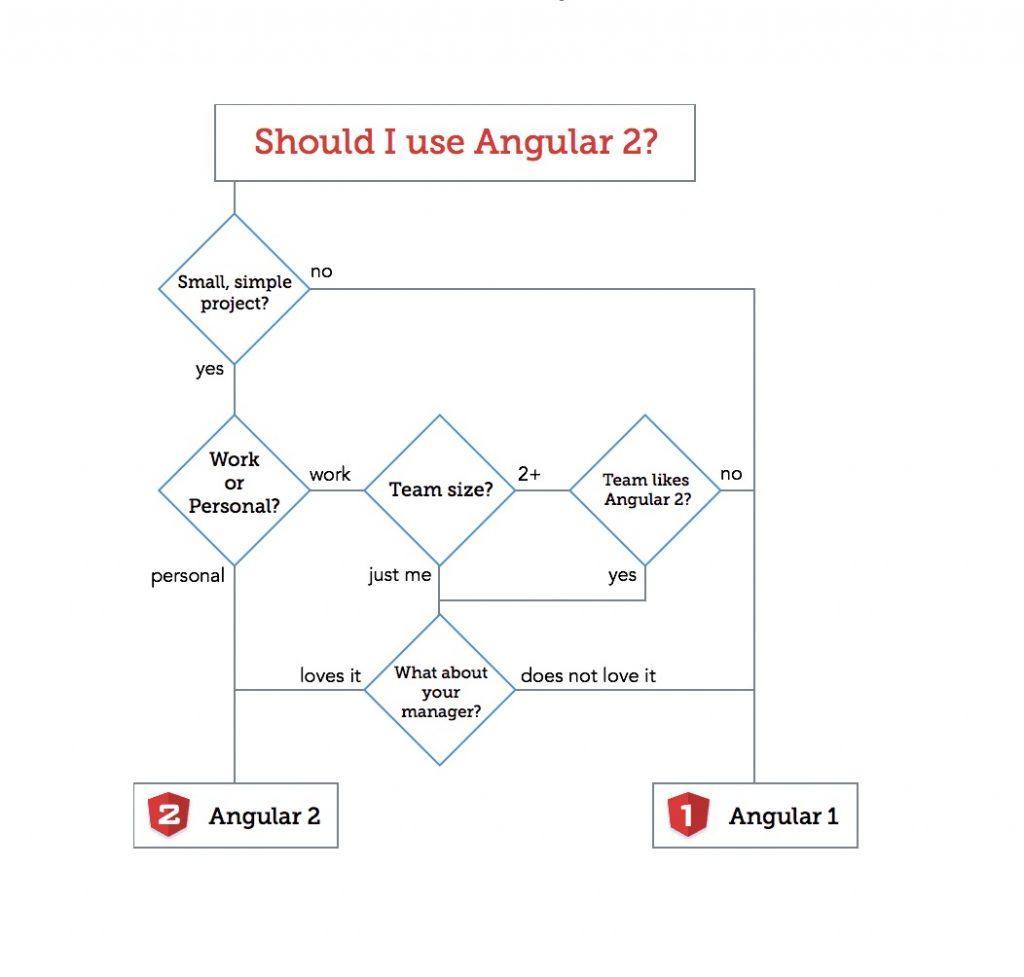
Angular is the most popular JavaScript framework of 2025. Today we are discussing the most asked question about Angular vs Angular 2 which version a developer should choose for AngularJS web development… Stay Tuned till the end!
The world is evolving rapidly over the past few years. The sector has been through so many innovations, but all of that came at a cost of developer convenience.
Concerning Angular was developed at a time when web technologies like Javascript, HTML, etc were just in the initial stage of their evolution. The core ideas, which were implemented were ahead of their time, and many of them have now become international standards.
So, the developers had to make a choice whether they stuck up with their current architectures and attempt to mold them over the new standards or just start from scratch building around the new standards.
Also, AngularJS and Node.js are the most popular JavaScript frameworks but it is hard to know which one to choose for web application development and business. if you are thinking for creating a web app by using angularjs, then first you need to know whether AngularJS SEO friendly or not.
As a result, Angular 2 came into sight in mid-2016. They use the Hierarchical Dependency Injection system, which is the main performance booster of the framework. It works by implementing unidirectional tree-based change detection, which also works as a performance booster.
According to the developers, Angular 2.0 is 5 times faster than its previous version and is also a huge learning curve for developers. It is completely developed in Typewrite and also meets the ES6 specification. You must not fall into the misconception that it is an update for Angular, It is completely rewritten and includes many changes.
Before getting into differences between Angular and Angular 2 check out what is new in Angular 15 and how to upgrade it?
Difference: Angular vs Angular 2
Let’s have a look at a comparison of Angular vs Angular 2 –
-
Angular 2 is mobile-oriented and better in performance
Angular 1 was introduced long ago and was not built with mobile support in mind, whereas, being introduced in the current era, Angular 2.0 comes with features of mobile support.
Angular 2 uses a Hierarchical Dependency Injection system and implements unidirectional tree-based change detection, which acts as a major performance booster for the framework.
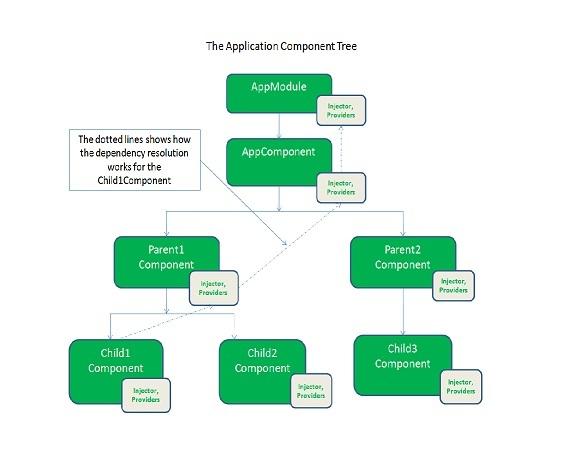
According to the developers, Angular 2 is 5 times faster than Angular 1.
-
Angular 2 offers more choices for languages
Angular 2 offers more choices for languages such as ES5, ES6, TypeScript, or Dart for writing codes, whereas, Angular 1 only offers ES5, ES6, and Dart for writing codes. Using Typescript is a recommendable step, as it is an awesome way to write Javascript codes.
-
Angular 2 implements web standard-like components
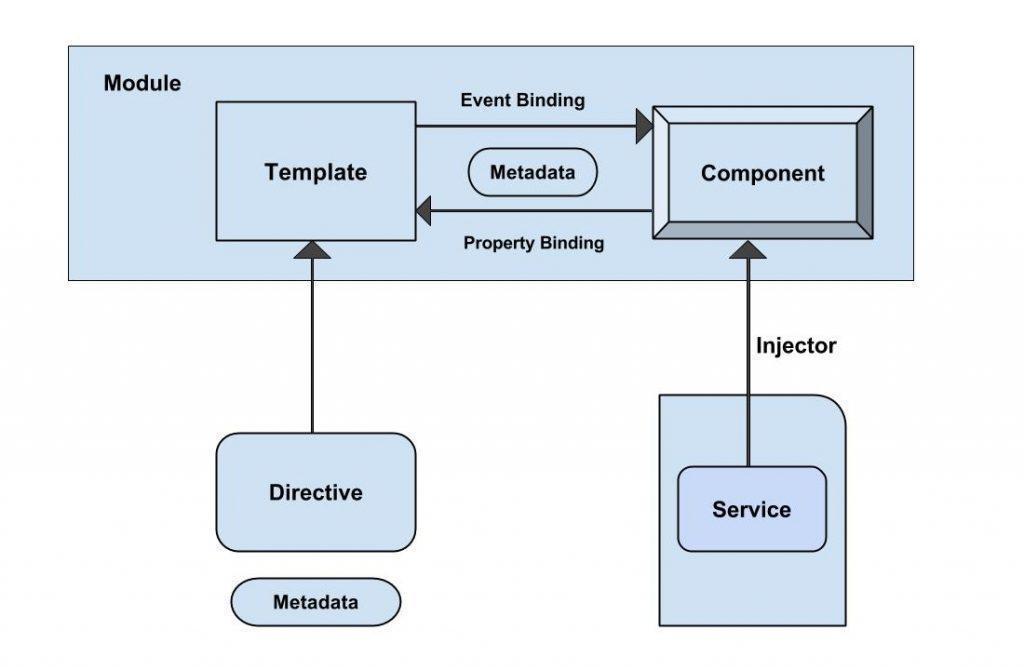
It implements web standard-like components and provides better performance than Angular
-
Angular 2 is not as easy to set up as Angular 1
Angular 2 is a bit complicated to set up as compared to Angular 1. In Angular, you just need to add a reference of a library to get started, whereas, Angular 2 is totally dependent on additional libraries and requires efforts to set it up.
Angular:
Angular 2:
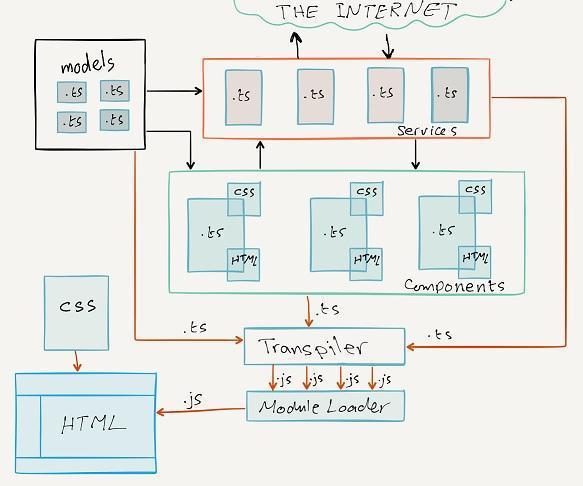
-
Angular 1 controllers and $scope are gone
The controllers and $scope in Angular 1 have been replaced with “Components” in Angular 2. Hence we can say that it is a component-based framework, which uses zone.js to detect changes.
Angular controllers:
var myApp = angular.module('myApp',[]);
myApp.controller('GreetingController', ['$scope', function($scope) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello!';
}]);
Angular 2 Components:
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<h2>My Heroes</h2>
<ul class="heroes">
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes"
[class.selected]="hero === selectedHero"
(click)="onSelect(hero)">
<span class="badge">{{hero.id}}</span> {{hero.name}}
</li>
</ul>
<hero-detail [hero]="selectedHero"></hero-detail>
`,
-
Different ways to define local variables
In Angular 2, the ways of defining local variables have been changed a bit as compared to Angular. Angular 2 now uses the Hash (#) prefix to define local variables.
<div *ngFor="#SAGIPL of sagipl">
-
Structural directives syntax is changed
Structural directives syntax has been changed in Angular 2. For example, ng-repeat has been replaced with ng for.
-
Angular 2 uses camelCase syntax for built-in directives
CamelCase syntax is used in Angular 2 for built-in directives. For example, ng-model has been changed to ngModel, and ng-class is now ngClass.
Angular structural directives:
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="framework in frameworks">
{{framework.name}}
</li>
</ul>
Angular 2 structural directives:
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="#framework in frameworks">
{{framework.name}}
</li>
</ul>
-
Angular 2, directly uses valid HTML DOM events and element properties
One of the biggest highlights of Angular 2 is that it is capable of directly using valid HTML DOM element events and properties. Of this, most of the built-in directives in Angular 1, which include ng-herf, ng-src, ng-show, and ng-hide are no longer required. Angular 2 uses src, herf, and hidden properties to get exactly the same output.
For Example-
<button ng-click="doinggood()">
in Angular 2
<button (click)="doinggood()">
-
One-way data binding directive replaced with (property).
In Angular, ng-bind used to be implemented for one-way data binding, but in Angular 2, it is replaced with (property), where the property plays the role of a valid HTML DOM element property.
<input ng-bind="framework.name"></input>
in Angular 2
<button (click)="doinggood()">
-
Two-way data binding: ng-model replaced with ngModel
In Angular, ng-model is used for two-way data binding, which has now been replaced with ngModel in Angular 2.
<input ng-model="framework.name"></input>
in Angular 2
<input [(ngModel)]="framework.name"></input>
-
The way of Bootstrapping Angular Applications is changed
There are two ways to bootstrap Angular, of which one can be done using the ng-app attribute and the other via coding.
But in Angular 2, there is only one way to bootstrap, and that is via coding.
import { bootstrap } from 'angular2/platform/browser';
import { ProductComponent } from './product.component';
bootstrap(ProductComponent);
-
Ways of Dependency Injection are changed
Dependency Injection is one more advantage of Angular 2. As we know everything is ‘class’ in Angular 2, hence Dependency Injection can only be achieved via constructors.
Angular
angular.module('myModule', [])
.factory('serviceId', ['depService', function(depService) {
// ...
}])
.directive('directiveName', ['depService', function(depService) {
// ...
}])
.filter('filterName', ['depService', function(depService) {
// ...
}]);
Angular 2
import { Injectable } from 'angular2/core';
@Injectable()
export class JavascriptFrameworks {
constructor(private _http: Http) { }
getTechnologies() {
return [new framework(1, 'Angular'),
new framework(2, 'jQuery',
new framework(3, 'Node'),
new framework(4, 'Knockout')
];
}
}
-
The way of routing is changed
In Angular 2, @RouteConfig{(…)} is used in the place of $routeprovider.when(), which was used in Angular to configure routing.
Conclusion
Angular 2 undoubtedly has very powerful routes, and it only loads components when it strictly requires them.
It requires more effort to migrate from Angular to Angular 2, but it is more reliable and comfortable to work with as compared to Angular.







